Armenia
Armenia is a small, upper-middle-income country located in the South Caucasus with a GDP of12.6 Billion USD. Armenia is mountainous country, most of its area is at the elevation above1,000 meters (3,300 feet) above the sea level. (Figure 1). The climate of Armenia is continental, with cold winters and hot summers. The precipitation is not abundant. The population of Armenia is approximately 3 million people. The country has 11 marzes (provinces) with diverse geographical features (plains, valleys, hills, and high mountains). The rural population is about 1 million people (about 37 % of total population).
Armenia has a number of environmental issues, including:
- Contamination with toxic heavy metals from mining and ore processing activities. There are both legacy and active highly contaminated mining sites
- Hazardous waste – including industrial, electronic and chemical waste, is currently mixed with municipal waste, leading to toxic pollution of soil and water, long-term and composite damage to the environment
- POPs – During the Soviet era Armenia had a developed agricultural production and was amongst the regions with intense pesticide application. The total area load of pesticides averaged 9-35.5 kg ha-1, exceeding the average levels of pesticide application. Organochlorine pesticides were widely applied in Armenia until the ban in 1980s.
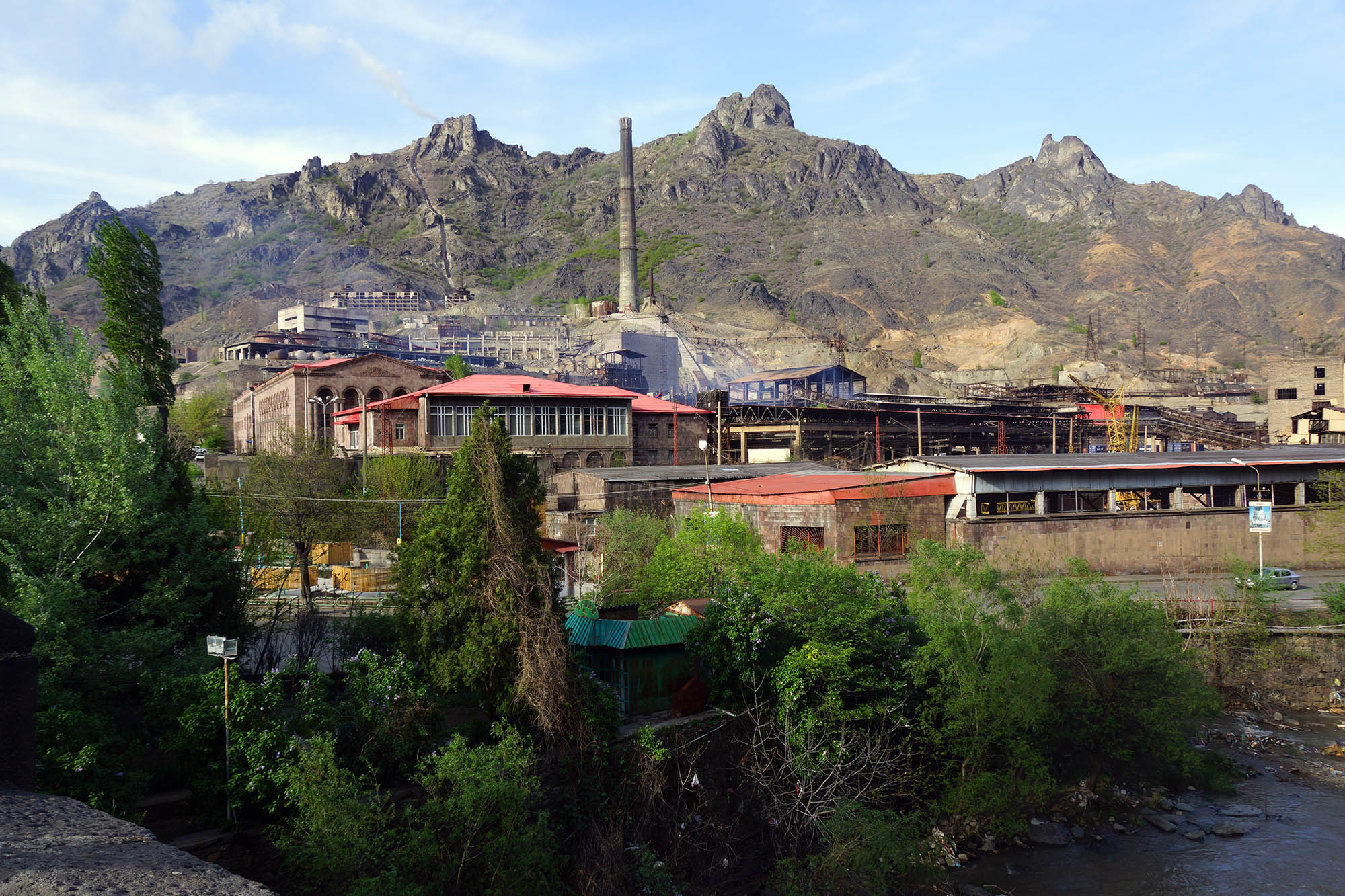


Implemented projects:
- Akhtala Monastery cleanup program
- Toxic Sites Identification Program (TSIP) in Armenia (dumpsites)
- Preliminary and Deep Site Assessment in Abovyan dumpsite
Proposed future projects:
- Lead Health Risk Mitigation in Akhtala
- Lead Health Risk Assessment in Alaverdi
- Assessment of hazardous waste (arsenic graveyard) and planning reconstruction/cleanup in marz Lori
- Assessment of several areas contaminated with pesticides, cleanup

